一、Algorithm
1、Validate-IP-Address
leetcode-468-Validate-IP-Address
Write a function to check whether an input string is a valid IPv4 address or IPv6 address or neither.
IPv4 addresses are canonically represented in dot-decimal notation, which consists of four decimal numbers, each ranging from 0 to 255, separated by dots ("."), e.g.,172.16.254.1;
Besides, leading zeros in the IPv4 is invalid. For example, the address 172.16.254.01 is invalid.
IPv6 addresses are represented as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits, each group representing 16 bits. The groups are separated by colons (":"). For example, the address 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334 is a valid one. Also, we could omit some leading zeros among four hexadecimal digits and some low-case characters in the address to upper-case ones, so 2001:db8:85a3:0:0:8A2E:0370:7334 is also a valid IPv6 address(Omit leading zeros and using upper cases).
However, we don't replace a consecutive group of zero value with a single empty group using two consecutive colons (::) to pursue simplicity. For example, 2001:0db8:85a3::8A2E:0370:7334 is an invalid IPv6 address.
Besides, extra leading zeros in the IPv6 is also invalid. For example, the address 02001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334 is invalid.
Note: You may assume there is no extra space or special characters in the input string.
Example 1:
Input: "172.16.254.1"
Output: "IPv4"
Explanation: This is a valid IPv4 address, return "IPv4".
Example 2:
Input: "2001:0db8:85a3:0:0:8A2E:0370:7334"
Output: "IPv6"
Explanation: This is a valid IPv6 address, return "IPv6".
Example 3:
Input: "256.256.256.256"
Output: "Neither"
Explanation: This is neither a IPv4 address nor a IPv6 address.
class Solution:
def validIPAddress(self, IP: str) -> str:
import re
IPv4_pattern = r"^(((\d|[1-9]\d|1[\d]{2})|(2[0-4]\d)|(25[0-5]))\.){3}((\d|[1-9]\d|1[\d]{2})|(2[0-4]\d)|(25[0-5]))$"
IPv6_pattern = r"^([0-9a-f]{1,4}:){7}[0-9a-f]{1,4}$"
if re.match(IPv4_pattern, IP,re.I):
return "IPv4"
elif re.match(IPv6_pattern, IP,re.I):
return "IPv6"
else:
return "Neither"
# 补充:压缩格式IPv6判断
# def is_IPv6(ip: str):
# if "::" in ip and ip.count(":") <= 7:
# ip = (ip[:ip.index("::")+1] if len(ip[:ip.index("::")]) > 0 else "") + \
# (":".join("0" for _ in range(8-len(list(filter(lambda x: len(x) > 0, ip.split(":"))))))) + \
# (ip[ip.index("::") + 1:] if len(ip[ip.index("::") + 2:]) > 0 else "")
#
# IPv6_pattern = r"([0-9a-f]{1,4}:){7}[0-9a-f]{1,4}"
# return bool(re.match(IPv6_pattern, ip, re.I))
2、合并数组中相交的区间
const arr = [ [1, 4], [3, 6], [9, 13], [6, 20], [30, 50] ];
// 输出 [[1, 20], [30, 50]]
// 其中 [1, 4] 表示区间大于等于1,小于等于4的区间
# python3
# Input: arr = [[1, 4], [3, 6], [9, 13], [6, 20], [30, 50]]
# Output: [[1, 20], [30, 50]]
# Input: arr = [[3, 6], [1, 4], [9, 13], [30, 50], [6, 20], [70, 100], [33, 33], [-11, 2], [80, 120], [80, 90]]
# Output: [[-11, 20], [30, 50], [70, 120]]
def merge_intersected_arrays(arr: list):
"""
先对数组按首位元素排序,然后对有序数组用两层循环做遍历合并,并将最大值放在当次循环首个比较值中;用bool数组标记是否是被合并项,避免重复比较
时间复杂度 O(nlogn+n^2 )≈O(n^2)
"""
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
arr.sort(key=lambda x: x[0])
b = [0] * len(arr)
for i in range(len(arr)):
if b[i]:
continue
for j in range(i + 1, len(arr)):
if arr[i][1] >= arr[j][0]:
arr[i][1] = max(arr[i][1], arr[j][1])
b[j] = 1
return list(arr[i] for i in range(len(b)) if not b[i])
二、Review
Django-form
Django-form-3.0 对照着汉化版的Django-form-2.2-zh读的
用django-form是对表单的综合处理,只需要处理forms、html和view,就能高效生成表单和校验逻辑
# forms.py
from django import forms
class NameForm(forms.Form):
your_name = forms.CharField(label='Your name', max_length=100)
# html
<form action="/your-name/" method="post">
{\% csrf_token \%}
{\{ form \}}
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
# view.py
from django.http import HttpResponseRedirect
from django.shortcuts import render
from .forms import NameForm
def get_name(request):
# if this is a POST request we need to process the form data
if request.method == 'POST':
# create a form instance and populate it with data from the request:
form = NameForm(request.POST)
# check whether it's valid:
if form.is_valid():
# process the data in form.cleaned_data as required
# ...
# redirect to a new URL:
return HttpResponseRedirect('/thanks/')
# if a GET (or any other method) we'll create a blank form
else:
form = NameForm()
return render(request, 'name.html', {'form': form})
三、Tip
yield
看到一道面试题,觉得很有意思
阅读以下代码,推导最后结果:
def add(n, i):
return n+i
def test():
for i in range(4):
yield i
g = test()
for n in [1, 10, 5]:
g = (add(n, i) for i in g)
print(list(g))
答案: [15, 16, 17, 18]
n = 1
g = (add(n,i) for i in test())
# print(list(g)) # [1, 2, 3, 4]
n = 10
g = (add(n,i) for i in (add(n,i) for i in test()))
# print(list(g)) # [20, 21, 22, 23]
n = 5
g = (add(n,i) for i in (add(n,i) for i in (add(n,i) for i in test())))
g = (add(n,i) for i in (add(n,i) for i in (5,6,7,8)))
g = (add(n,i) for i in (10,11,12,13))
g = (15,16,17,18)
print(list(g)) # [15, 16, 17, 18]
考察yield使用,所有的结果都是生成器表达式,不调用它,不从里面取值,就不干活
可参照python中yield的用法详解——最简单,最清晰的解释
四、Share
PC兼容性测试
周一领导安排部门开展兼容性测试并提供了用户实际使用浏览器统计表,大致如下: 结果显示Chrome占大头,其次Top5是QQ浏览器、搜狗浏览器、Safari、猎豹浏览器和FireFox,360占比很低,这点我觉得与实际不符,360市场占有率应该是很高的
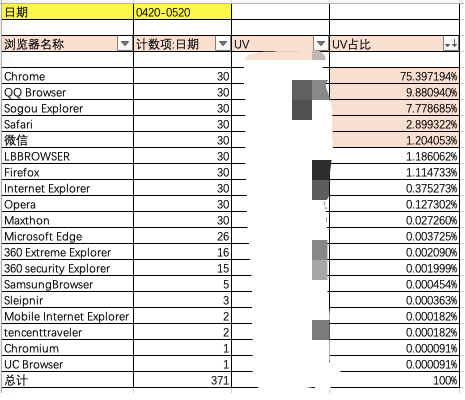
两年前根据nginx访问日志中的UA,我就对官网的浏览器类型做过分析,大致分布和本次一致,不过当时也没办法把360单独统计出来。
其中因为所有的UA中都含有Chrome的UA,所以无法判断出具体Chrome的占比,但是能通过排除法,确定占比。其中360急速模式和Chrome的UA一模一样,无法单独分离,就市面上的统计数据而言,360是Chrome外占比最大的浏览器。
| 浏览器内核类型 | 占比 |
|---|---|
| Chrome内核 | ? |
| QQ浏览器 | 10.79% |
| 搜狗浏览器极速模式 | 7.26% |
| edge | 4.94% |
| 360兼容模式 | 3.05 % |
| 2345浏览器 | 2.8% |
| safari | 2.75% |
| 猎豹浏览器 | 2.14% |
| UC浏览器 | 1.52% |
| 百度浏览器 | 0.33% |
| 搜狗浏览器兼容模式 | 0.16% |
| 其余类型浏览器 | <0.1% |
一提到兼容性测试,就不得不做浏览器选型
- 考虑到QQ、搜狗、猎豹都是双核浏览器,既有极速模式(webkit内核(渲染引擎)),又有兼容模式(Trident内核(渲染引擎),和一致),那就挑一款做极速模式测试,一款做兼容模式测试
- Safari虽然和Chrome的内核渲染引擎都是webkit,但是Chrome的js引擎是V8,Safari的js引擎是Nitro,导致它们两个在解释执行js时结果不一致,所以Safari必然是要测试的
- FireFox内核(渲染引擎)是Gecko,也需要单独测试
所以最终测试选型是:
Windows: QQ浏览器-极速模式 - 版本号 (Webkit)
Windows: 搜狗浏览器 - 兼容模式 - 版本号 (Trident)
Windows: 火狐浏览器(Firefox) - 版本号 (Gecko)
Mac: Safari -版本号 - (Webkit,Nitro)